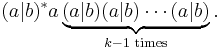Regular expression
In computing, regular expressions, also referred to as regex or regexp, provide a concise and flexible means for matching strings of text, such as particular characters, words, or patterns of characters. A regular expression is written in a formal language that can be interpreted by a regular expression processor, a program that either serves as a parser generator or examines text and identifies parts that match the provided specification.
The following examples illustrate a few specifications that could be expressed in a regular expression:
- The sequence of characters "car" in any context, such as "car", "cartoon", or "bicarbonate"
- The word "car" when it appears as an isolated word
- The word "car" when preceded by the word "blue" or "red"
- A dollar sign immediately followed by one or more digits, and then optionally a period and exactly two more digits (for example "$10", or "$245.99").
Regular expressions can be much more complex than these examples.
Regular expressions are used by many text editors, utilities, and programming languages to search and manipulate text based on patterns. For example, most scripting languages, such as Perl, Ruby, Awk and Tcl have regular expression engines built directly into their syntax. Several utilities provided by Unix distributions—including the editor ed and the filter grep—were the first to popularize the concept of regular expressions.
As an example of the syntax, the regular expression \bex can be used to search for all instances of the string "ex" that occur after "word boundaries" (signified by the \b). In layman's terms, \bex will find the matching string "ex" in two possible locations, (1) at the beginning of words, and (2) between two characters in a string, where one is a word character and the other is not a word character. Thus, in the string "Texts for experts," \bex matches the "ex" in "experts" but not in "Texts" (because the "ex" occurs inside a word and not immediately after a word boundary).
Many modern computing systems provide wildcard characters in matching filenames from a file system. This is a core capability of many command-line shells and is also known as globbing. Wildcards differ from regular expressions in generally only expressing very limited forms of alternatives.
Contents |
Basic concepts
A regular expression, often called a pattern, is an expression that describes a set of strings. They are usually used to give a concise description of a set, without having to list all elements. For example, the set containing the three strings "Handel", "Händel", and "Haendel" can be described by the pattern H(ä|ae?)ndel (or alternatively, it is said that the pattern matches each of the three strings). In most formalisms, if there is any regex that matches a particular set then there is an infinite number of such expressions. Most formalisms provide the following operations to construct regular expressions.
- Boolean "or"
- A vertical bar separates alternatives. For example,
gray|greycan match "gray" or "grey". - Grouping
- Parentheses are used to define the scope and precedence of the operators (among other uses). For example,
gray|greyandgr(a|e)yare equivalent patterns which both describe the set of "gray" and "grey". - Quantification
- A quantifier after a token (such as a character) or group specifies how often that preceding element is allowed to occur. The most common quantifiers are the question mark
?, the asterisk*(derived from the Kleene star), and the plus sign+.
-
?The question mark indicates there is zero or one of the preceding element. For example, colou?rmatches both "color" and "colour".*The asterisk indicates there are zero or more of the preceding element. For example, ab*cmatches "ac", "abc", "abbc", "abbbc", and so on.+The plus sign indicates that there is one or more of the preceding element. For example, ab+cmatches "abc", "abbc", "abbbc", and so on, but not "ac".
These constructions can be combined to form arbitrarily complex expressions, much like one can construct arithmetical expressions from numbers and the operations +, −, ×, and ÷. For example, H(ae?|ä)ndel and H(a|ae|ä)ndel are both valid patterns which match the same strings as the earlier example, H(ä|ae?)ndel.
The precise syntax for regular expressions varies among tools and with context; more detail is given in the Syntax section.
History
The origins of regular expressions lie in automata theory and formal language theory, both of which are part of theoretical computer science. These fields study models of computation (automata) and ways to describe and classify formal languages. In the 1950s, mathematician Stephen Cole Kleene described these models using his mathematical notation called regular sets.[1] The SNOBOL language was an early implementation of pattern matching, but not identical to regular expressions. Ken Thompson built Kleene's notation into the editor QED as a means to match patterns in text files. He later added this capability to the Unix editor ed, which eventually led to the popular search tool grep's use of regular expressions ("grep" is a word derived from the command for regular expression searching in the ed editor: g/re/p where re stands for regular expression[2]). Since that time, many variations of Thompson's original adaptation of regular expressions have been widely used in Unix and Unix-like utilities including expr, AWK, Emacs, vi, and lex.
Perl and Tcl regular expressions were derived from a regex library written by Henry Spencer, though Perl later expanded on Spencer's library to add many new features.[3] Philip Hazel developed PCRE (Perl Compatible Regular Expressions), which attempts to closely mimic Perl's regular expression functionality and is used by many modern tools including PHP and Apache HTTP Server. Part of the effort in the design of Perl 6 is to improve Perl's regular expression integration, and to increase their scope and capabilities to allow the definition of parsing expression grammars.[4] The result is a mini-language called Perl 6 rules, which are used to define Perl 6 grammar as well as provide a tool to programmers in the language. These rules maintain existing features of Perl 5.x regular expressions, but also allow BNF-style definition of a recursive descent parser via sub-rules.
The use of regular expressions in structured information standards for document and database modeling started in the 1960s and expanded in the 1980s when industry standards like ISO SGML (precursored by ANSI "GCA 101-1983") consolidated. The kernel of the structure specification language standards are regular expressions. Simple use is evident in the DTD element group syntax.
See also Pattern matching: History.
Formal language theory
Definition
Regular expressions describe regular languages in formal language theory. They have thus the same expressive power as regular grammars. Regular expressions consist of constants and operators that denote sets of strings and operations over these sets, respectively. The following definition is standard, and found as such in most textbooks on formal language theory.[5][6] Given a finite alphabet Σ, the following constants are defined:
- (empty set) ∅ denoting the set ∅.
- (empty string) ε denoting the set containing only the "empty" string, which has no characters at all.
- (literal character)
ain Σ denoting the set containing only the character a.
The following operations are defined:
- (concatenation) RS denoting the set { αβ | α in R and β in S }. For example {"ab", "c"}{"d", "ef"} = {"abd", "abef", "cd", "cef"}.
- (alternation) R | S denoting the set union of R and S. For example {"ab", "c"}|{"ab", "d", "ef"} = {"ab", "c", "d", "ef"}.
- (Kleene star) R* denoting the smallest superset of R that contains ε and is closed under string concatenation. This is the set of all strings that can be made by concatenating zero or more strings in R. For example, {"ab", "c"}* = {ε, "ab", "c", "abab", "abc", "cab", "cc", "ababab", "abcab", ... }.
To avoid parentheses it is assumed that the Kleene star has the highest priority, then concatenation and then set union. If there is no ambiguity then parentheses may be omitted. For example, (ab)c can be written as abc, and a|(b(c*)) can be written as a|bc*. Many textbooks use the symbols ∪, +, or ∨ for alternation instead of the vertical bar.
Examples:
a|b*denotes {ε, a, b, bb, bbb, ...}(a|b)*denotes the set of all strings with no symbols other than a and b, including the empty string: {ε, a, b, aa, ab, ba, bb, aaa, ...}ab*(c|ε)denotes the set of strings starting with a, then zero or more bs and finally optionally a c: {a, ac, ab, abc, abb, abbc, ...}
Expressive power and compactness
The formal definition of regular expressions is purposely parsimonious and avoids defining the redundant quantifiers ? and +, which can be expressed as follows: a+ = aa*, and a? = (a|ε). Sometimes the complement operator is added, to give a generalized regular expression; here Rc matches all strings over Σ* that do not match R. In principle, the complement operator is redundant, as it can always be circumscribed by using the other operators. However, the process for computing such a representation is complex, and the result may require expressions of a size that is double exponentially larger.[7][8]
Regular expressions in this sense can express the regular languages, exactly the class of languages accepted by deterministic finite automata. There is, however, a significant difference in compactness. Some classes of regular languages can only be described by deterministic finite automata whose size grows exponentially in the size of the shortest equivalent regular expressions. The standard example are here the languages Lk consisting of all strings over the alphabet {a,b} whose kth-last letter equals a. On the one hand, a regular expression describing L4 is given by 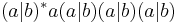 . Generalizing this pattern to Lk gives the expression
. Generalizing this pattern to Lk gives the expression
On the other hand, it is known that every deterministic finite automaton accepting the language Lk must have at least 2k states. Luckily, there is a simple mapping from regular expressions to the more general nondeterministic finite automata (NFAs) that does not lead to such a blowup in size; for this reason NFAs are often used as alternative representations of regular languages. NFAs are a simple variation of the type-3 grammars of the Chomsky hierarchy.[5]
Finally, it is worth noting that many real-world "regular expression" engines implement features that cannot be described by the regular expressions in the sense of formal language theory; see below for more on this.
Deciding equivalence of regular expressions
As the examples show, different regular expressions can express the same language: the formalism is redundant.
It is possible to write an algorithm which for two given regular expressions decides whether the described languages are essentially equal, reduces each expression to a minimal deterministic finite state machine, and determines whether they are isomorphic (equivalent).
To what extent can this redundancy be eliminated? Kleene star and set union are required to find an interesting subset of regular expressions that is still fully expressive?, but perhaps their use can be restricted. This is a surprisingly difficult problem. As simple as the regular expressions are, there is no method to systematically rewrite them to some normal form. The lack of axiom in the past led to the star height problem. Recently, Dexter Kozen axiomatized regular expressions with Kleene algebra.[9]
Syntax
A number of special characters or metacharacters are used to denote actions or delimit groups; but it is possible to force these special characters to be interpreted as normal characters by preceding them with a defined escape character, usually the backslash "\". For example, a dot is normally used as a "wild card" metacharacter to denote any character, but if preceded by a backslash it represents the dot character itself. The expression "c.t" matches "cat", "cot", "cut" and non-words such as "czt" and "c.t"; but "c\.t" matches only "c.t". The backslash also escapes itself, i.e., two backslashes are interpreted as the backslash character.
POSIX
POSIX Basic Regular Expressions
Traditional Unix regular expression syntax followed common conventions but often differed from tool to tool. The IEEE POSIX Basic Regular Expressions (BRE) standard (released alongside an alternative flavor called Extended Regular Expressions or ERE) was designed mostly for backward compatibility with the traditional (Simple Regular Expression) syntax but provided a common standard which has since been adopted as the default syntax of many Unix regular expression tools, though there is often some variation or additional features. Many such tools also provide support for ERE syntax with command line arguments.
In the BRE syntax, most characters are treated as literals — they match only themselves (i.e., a matches "a"). The exceptions, listed below, are called metacharacters or metasequences.
| Metacharacter | Description |
|---|---|
. |
Matches any single character (many applications exclude newlines, and exactly which characters are considered newlines is flavor, character encoding, and platform specific, but it is safe to assume that the line feed character is included). Within POSIX bracket expressions, the dot character matches a literal dot. For example, a.c matches "abc", etc., but [a.c] matches only "a", ".", or "c". |
[ ] |
A bracket expression. Matches a single character that is contained within the brackets. For example, [abc] matches "a", "b", or "c". [a-z] specifies a range which matches any lowercase letter from "a" to "z". These forms can be mixed: [abcx-z] matches "a", "b", "c", "x", "y", or "z", as does [a-cx-z].
The |
[^ ] |
Matches a single character that is not contained within the brackets. For example, [^abc] matches any character other than "a", "b", or "c". [^a-z] matches any single character that is not a lowercase letter from "a" to "z". As above, literal characters and ranges can be mixed. |
^ |
Matches the starting position within the string. In line-based tools, it matches the starting position of any line. |
$ |
Matches the ending position of the string or the position just before a string-ending newline. In line-based tools, it matches the ending position of any line. |
BRE: \( \)ERE: ( ) |
Defines a marked subexpression. The string matched within the parentheses can be recalled later (see the next entry, \n). A marked subexpression is also called a block or capturing group. |
\n |
Matches what the nth marked subexpression matched, where n is a digit from 1 to 9. This construct is theoretically irregular and was not adopted in the POSIX ERE syntax. Some tools allow referencing more than nine capturing groups. |
* |
Matches the preceding element zero or more times. For example, ab*c matches "ac", "abc", "abbbc", etc. [xyz]* matches "", "x", "y", "z", "zx", "zyx", "xyzzy", and so on. \(ab\)* matches "", "ab", "abab", "ababab", and so on. |
BRE: \{m,n\}ERE: {m,n} |
Matches the preceding element at least m and not more than n times. For example, a\{3,5\} matches only "aaa", "aaaa", and "aaaaa". This is not found in a few older instances of regular expressions. |
Examples:
.atmatches any three-character string ending with "at", including "hat", "cat", and "bat".[hc]atmatches "hat" and "cat".[^b]atmatches all strings matched by.atexcept "bat".^[hc]atmatches "hat" and "cat", but only at the beginning of the string or line.[hc]at$matches "hat" and "cat", but only at the end of the string or line.\[.\]matches any single character surrounded by "[" and "]" since the brackets are escaped, for example: "[a]" and "[b]".
POSIX Extended Regular Expressions
The meaning of metacharacters escaped with a backslash is reversed for some characters in the POSIX Extended Regular Expression (ERE) syntax. With this syntax, a backslash causes the metacharacter to be treated as a literal character. So, for example, \( \) is now ( ) and \{ \} is now { }. Additionally, support is removed for \n backreferences and the following metacharacters are added:
| Metacharacter | Description |
|---|---|
? |
Matches the preceding element zero or one time. For example, ba? matches "b" or "ba". |
+ |
Matches the preceding element one or more times. For example, ba+ matches "ba", "baa", "baaa", and so on. |
| |
The choice (aka alternation or set union) operator matches either the expression before or the expression after the operator. For example, abc|def matches "abc" or "def". |
Examples:
[hc]+atmatches "hat", "cat", "hhat", "chat", "hcat", "ccchat", and so on, but not "at".[hc]?atmatches "hat", "cat", and "at".[hc]*atmatches "hat", "cat", "hhat", "chat", "hcat", "ccchat", "at", and so on.cat|dogmatches "cat" or "dog".
POSIX Extended Regular Expressions can often be used with modern Unix utilities by including the command line flag -E.
POSIX character classes
Since many ranges of characters depend on the chosen locale setting (i.e., in some settings letters are organized as abc...zABC...Z, while in some others as aAbBcC...zZ), the POSIX standard defines some classes or categories of characters as shown in the following table:
| POSIX | Non-standard | Perl | ASCII | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
[:alnum:] |
[A-Za-z0-9] |
Alphanumeric characters | ||
[:word:] |
\w |
[A-Za-z0-9_] |
Alphanumeric characters plus "_" | |
\W |
[^A-Za-z0-9_] |
Non-word characters | ||
[:alpha:] |
[A-Za-z] |
Alphabetic characters | ||
[:blank:] |
[ \t] |
Space and tab | ||
[:cntrl:] |
[\x00-\x1F\x7F] |
Control characters | ||
[:digit:] |
\d |
[0-9] |
Digits | |
\D |
[^0-9] |
Non-digits | ||
[:graph:] |
[\x21-\x7E] |
Visible characters | ||
[:lower:] |
[a-z] |
Lowercase letters | ||
[:print:] |
[\x20-\x7E] |
Visible characters and spaces | ||
[:punct:] |
[-!"#$%&'()*+,./:;<=>?@[\\\]^_`{|}~] |
Punctuation characters | ||
[:space:] |
\s |
[ \t\r\n\v\f] |
Whitespace characters | |
\S |
[^ \t\r\n\v\f] |
Non-whitespace characters | ||
[:upper:] |
[A-Z] |
Uppercase letters | ||
[:xdigit:] |
[A-Fa-f0-9] |
Hexadecimal digits |
POSIX character classes can only be used within bracket expressions. For example, [[:upper:]ab] matches the uppercase letters and lowercase "a" and "b".
In Perl regular expressions, [:print:] matches [:graph:] union [:space:]. An additional non-POSIX class understood by some tools is [:word:], which is usually defined as [:alnum:] plus underscore. This reflects the fact that in many programming languages these are the characters that may be used in identifiers. The editor Vim further distinguishes word and word-head classes (using the notation \w and \h) since in many programming languages the characters that can begin an identifier are not the same as those that can occur in other positions.
Note that what the POSIX regular expression standards call character classes are commonly referred to as POSIX character classes in other regular expression flavors which support them. With most other regular expression flavors, the term character class is used to describe what POSIX calls bracket expressions.
Perl-derivative regular expressions
Perl has a more consistent and richer syntax than the POSIX basic (BRE) and extended (ERE) regular expression standards. An example of its consistency is that \ always escapes a non-alphanumeric character. Another example of functionality possible with Perl but not POSIX-compliant regular expressions is the concept of lazy quantification (see the next section).
Due largely to its expressive power, many other utilities and programming languages have adopted syntax similar to Perl's — for example, Java, JavaScript, PCRE, Python, Ruby, Microsoft's .NET Framework, and the W3C's XML Schema all use regular expression syntax similar to Perl's. Some languages and tools such as Boost and PHP support multiple regular expression flavors. Perl-derivative regular expression implementations are not identical, and many implement only a subset of Perl's features. With Perl 5.10, this process has come full circle with Perl incorporating syntax extensions originally from Python, PCRE, the .NET Framework, and Java.
Simple Regular Expressions
Simple Regular Expressions is a syntax that may be used by historical versions of application programs, and may be supported within some applications for the purpose of providing backward compatibility. It is deprecated.[10]
Lazy quantification
The standard quantifiers in regular expressions are greedy, meaning they match as much as they can, only giving back as necessary to match the remainder of the regex. For example, to find the first instance of an item between < and > symbols in this example:
Another whale sighting occurred on <January 26>, <2004>.
someone new to regexes would likely come up with the pattern <.*> or similar. However, instead of the "<January 26>" that might be expected, this pattern will actually return "<January 26>, <2004>" because the * quantifier is greedy — it will consume as many characters as possible from the input, and "January 26>, <2004" has more characters than "January 26".
Though this problem can be avoided in a number of ways (e.g., by specifying the text that is not to be matched: <[^>]*>), modern regular expression tools allow a quantifier to be specified as lazy (also known as non-greedy, reluctant, minimal, or ungreedy) by putting a question mark after the quantifier (e.g., <.*?>), or by using a modifier which reverses the greediness of quantifiers (though changing the meaning of the standard quantifiers can be confusing). By using a lazy quantifier, the expression tries the minimal match first. Though in the previous example lazy matching is used to select one of many matching results, in some cases it can also be used to improve performance when greedy matching would require more backtracking.
Patterns for non-regular languages
Many features found in modern regular expression libraries provide an expressive power that far exceeds the regular languages. For example, many implementations allow grouping subexpressions with parentheses and recalling the value they match in the same expression (backreferences). This means that a pattern can match strings of repeated words like "papa" or "WikiWiki", called squares in formal language theory. The pattern for these strings is (.*)\1.
The language of squares is not regular, nor is it context-free. Pattern matching with an unbounded number of back references, as supported by numerous modern tools, is NP-complete (see,[11] Theorem 6.2).
However, many tools, libraries, and engines that provide such constructions still use the term regular expression for their patterns. This has led to a nomenclature where the term regular expression has different meanings in formal language theory and pattern matching. For this reason, some people have taken to using the term regex or simply pattern to describe the latter. Larry Wall, author of the Perl programming language, writes in an essay about the design of Perl 6:
| “ | 'Regular expressions' [...] are only marginally related to real regular expressions. Nevertheless, the term has grown with the capabilities of our pattern matching engines, so I'm not going to try to fight linguistic necessity here. I will, however, generally call them "regexes" (or "regexen", when I'm in an Anglo-Saxon mood).[4] | ” |
Implementations and running times
There are at least three different algorithms that decide if and how a given regular expression matches a string.
The oldest and fastest two rely on a result in formal language theory that allows every nondeterministic finite automaton (NFA) to be transformed into a deterministic finite automaton (DFA). The DFA can be constructed explicitly and then run on the resulting input string one symbol at a time. Constructing the DFA for a regular expression of size m has the time and memory cost of O(2m), but it can be run on a string of size n in time O(n). An alternative approach is to simulate the NFA directly, essentially building each DFA state on demand and then discarding it at the next step, possibly with caching. This keeps the DFA implicit and avoids the exponential construction cost, but running cost rises to O(nm). The explicit approach is called the DFA algorithm and the implicit approach the NFA algorithm. As both can be seen as different ways of executing the same DFA, they are also often called the DFA algorithm without making a distinction. These algorithms are fast, but using them for recalling grouped subexpressions, lazy quantification, and similar features is tricky.[12][13]
The third algorithm is to match the pattern against the input string by backtracking. This algorithm is commonly called NFA, but this terminology can be confusing. Its running time can be exponential, which simple implementations exhibit when matching against expressions like (a|aa)*b that contain both alternation and unbounded quantification and force the algorithm to consider an exponentially increasing number of sub-cases. This behavior can cause a security problem called Regular expression Denial of Service - ReDoS, which might be used by hackers who want to attack a regular expression engine. More complex implementations will often identify and speed up or abort common cases where they would otherwise run slowly.
Although backtracking implementations only give an exponential guarantee in the worst case, they provide much greater flexibility and expressive power. For example, any implementation which allows the use of backreferences, or implements the various extensions introduced by Perl, must use a backtracking implementation.
Some implementations try to provide the best of both algorithms by first running a fast DFA match to see if the string matches the regular expression at all, and only in that case perform a potentially slower backtracking match.
Unicode
Regular expressions were originally used with ASCII characters. Many regular expression engines can now handle Unicode. In most respects it makes no difference what the character set is, but some issues do arise when extending regular expressions to support Unicode.
- Supported encoding. Some regular expression libraries expect the UTF-8 encoding, while others might expect UTF-16, or UTF-32.
- Supported Unicode range. Many regular expression engines support only the Basic Multilingual Plane, that is, the characters which can be encoded with only 16 bits. Currently, only a few regular expression engines can handle the full 21-bit Unicode range.
- Extending ASCII-oriented constructs to Unicode. For example, in ASCII-based implementations, character ranges of the form
[x-y]are valid wherever x and y are codepoints in the range [0x00,0x7F] and codepoint(x) ≤ codepoint(y). The natural extension of such character ranges to Unicode would simply change the requirement that the endpoints lie in [0x00,0x7F] to the requirement that they lie in [0,0x10FFFF]. However, in practice this is often not the case. Some implementations, such as that of gawk, do not allow character ranges to cross Unicode blocks. A range like [0x61,0x7F] is valid since both endpoints fall within the Basic Latin block, as is [0x0530,0x0560] since both endpoints fall within the Armenian block, but a range like [0x0061,0x0532] is invalid since it includes multiple Unicode blocks. Other engines, such as that of the Vim editor, allow block-crossing but limit the number of characters in a range to 128.
- Case insensitivity. Some case-insensitivity flags affect only the ASCII characters. Other flags affect all characters. Some engines have two different flags, one for ASCII, the other for Unicode. Exactly which characters belong to the POSIX classes also varies.
- Cousins of case insensitivity. As ASCII has case distinction, case insensitivity became a logical feature in text searching. Unicode introduced alphabetic scripts without case like Devanagari. For these, case sensitivity is not applicable. For scripts like Chinese, another distinction seems logical: between traditional and simplified. In Arabic scripts, insensitivity to initial, medial, final and isolated position may be desired. In Japanese, insensitivity between hiragana and katakana is sometimes useful.
- Normalization. Unicode introduced combining characters. Like old typewriters, plain letters can be followed by non-spacing accent symbols to form a single accented letter. As a consequence, two different code sequences can result in identical character display.
- New control codes. Unicode introduced amongst others, byte order marks and text direction markers. These codes might have to be dealt with in a special way.
- Introduction of character classes for Unicode blocks and Unicode general character properties. In Perl and the
java.util.regexlibrary, classes of the form\p{InX}match characters in block X and\P{InX}match the opposite. Similarly,\p{Armenian}matches any character in the Armenian block, and\p{X}matches any character with the general character property X. For example,\p{Lu}matches any upper-case letter.
Uses
Regular expressions are useful in the production of syntax highlighting systems, data validation, and many other tasks.
While regular expressions would be useful on search engines such as Google, processing them across the entire database could consume excessive computer resources depending on the complexity and design of the regex. Although in many cases system administrators can run regex-based queries internally, most search engines do not offer regex support to the public. Notable exceptions: Google Code Search, Exalead.
See also
- Comparison of regular expression engines
- Extended Backus–Naur Form
- List of regular expression software
- Regular expression examples
- Regular tree grammar
- Regular language
Notes
- ↑ Kleene (1956)
- ↑ Raymond, Eric S. citing Dennis Ritchie (2003). "Jargon File 4.4.7: grep". http://catb.org/jargon/html/G/grep.html.
- ↑ Wall, Larry and the Perl 5 development team (2006). "perlre: Perl regular expressions". http://perldoc.perl.org/perlre.html.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Wall (2002)
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Hopcroft, Motwani & Ullman (2000)
- ↑ Sipser (1998)
- ↑ Gelade & Neven (2008)
- ↑ Gruber & Holzer (2008)
- ↑ Kozen (1991)
- ↑ The Single Unix Specification (Version 2)
- ↑ Aho (1990)
- ↑ Cox (2007)
- ↑ Laurikari (2009)
References
- Aho, Alfred V. (1990). "Algorithms for finding patterns in strings". In van Leeuwen, Jan. Handbook of Theoretical Computer Science, volume A: Algorithms and Complexity. The MIT Press. pp. 255–300
- "Regular Expressions". The Single UNIX Specification, Version 2. The Open Group. 1997. http://www.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/007908799/xbd/re.html
- Cox, Russ (2007). "Regular Expression Matching Can Be Simple and Fast". http://swtch.com/~rsc/regexp/regexp1.html
- Forta, Ben (2004). Sams Teach Yourself Regular Expressions in 10 Minutes. Sams. ISBN 0-672-32566-7.
- Friedl, Jeffrey (2002). Mastering Regular Expressions. O'Reilly. ISBN 0-596-00289-0.
- Gelade, Wouter; Neven, Frank (2008). "Succinctness of the Complement and Intersection of Regular Expressions". Proceedings of the 25th International Symposium on Theoretical Aspects of Computer Science (STACS 2008). pp. 325–336. http://drops.dagstuhl.de/opus/volltexte/2008/1354
- Gruber, Hermann; Holzer, Markus (2008). "Finite Automata, Digraph Connectivity, and Regular Expression Size". Proceedings of the 35th International Colloquium on Automata, Languages and Programming (ICALP 2008). 5126. pp. 39–50. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-70583-3_4. http://www.informatik.uni-giessen.de/staff/gruber/data/icalp08.pdf
- Habibi, Mehran (2004). Real World Regular Expressions with Java 1.4. Springer. ISBN 1-59059-107-0.
- Hopcroft, John E.; Motwani, Rajeev; Ullman, Jeffrey D. (2000). Introduction to Automata Theory, Languages, and Computation (2nd ed.). Addison-Wesley.
- Kleene, Stephen C. (1956). "Representation of Events in Nerve Nets and Finite Automata". In Shannon, Claude E.; McCarthy, John. Automata Studies. Princeton University Press. pp. 3–42
- Kozen, Dexter (1991). "A Completeness Theorem for Kleene Algebras and the Algebra of Regular Events". Proceedings of the 6th Annual IEEE Symposium on Logic in Computer Science (LICS 1991). pp. 214–225
- Laurikari, Ville (2009). "TRE library 0.7.6". http://www.laurikari.net/tre/.
- Liger, Francois; Craig McQueen, Paul Wilton (2002). Visual Basic .NET Text Manipulation Handbook. Wrox Press. ISBN 1-86100-730-2.
- Sipser, Michael (1998). "Chapter 1: Regular Languages". Introduction to the Theory of Computation. PWS Publishing. pp. 31–90. ISBN 0-534-94728-X.
- Stubblebine, Tony (2003). Regular Expression Pocket Reference. O'Reilly. ISBN 0-596-00415-X.
- Wall, Larry (2002-06-04). "Apocalypse 5: Pattern Matching". http://dev.perl.org/perl6/doc/design/apo/A05.html.
External links
- Java Tutorials: Regular Expressions
- Perl Regular Expressions documentation
- VBScript and Regular Expressions
- .NET Framework Regular Expressions
- Regular Expressions at the Open Directory Project
- Pattern matching tools and libraries
- Structural Regular Expressions by Rob Pike
- JavaScript Regular Expressions Chapter and RegExp Object Reference at the Mozilla Developer Center